Cardiology is a medical specialty and a branch of internal medicine concerned with disorders of the heart. It deals with the diagnosis and treatment of such conditions as congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, electrophysiology, heart failure and valvular heart disease.
What is an ECG?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test to measure the electrical activity of the heart and record it onto a strip of paper. This may demonstrate problems with the heart’s rhythm and the conduction of the heart beat through the heart. It is also known as a 12 lead ECG.
Abnormalities of the ECG can be found in underlying heart disease or where there are rhythm disturbances of the heart. It may be useful in assessing how well the patient is responding to treatment.
An ECG may appear normal even in the presence of significant heart disease. Other tests are usually required in addition.
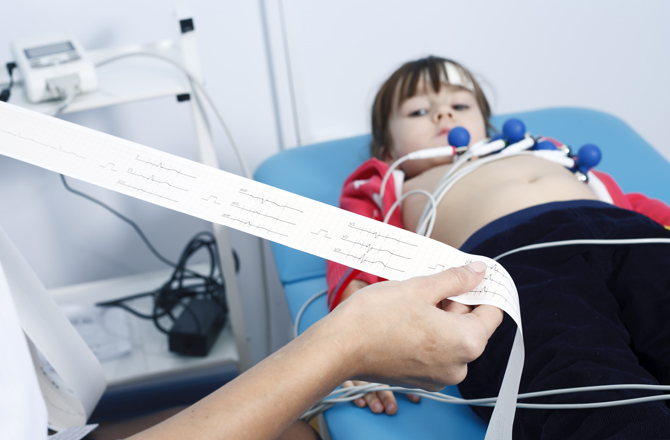
Twelve or thirteen self-adhesive patches are attached to various parts of the skin of the arms, legs and chest. Once the infant or child is still, the technician presses a button and the recording is taken. The test is painless and extremely quick once the leads are in position and the child still. After the test, the electrodes are removed. The doctor then reviews the paper print-out of the ECG.
What is a heart echocardiogram?
A heart echocardiogram is a test routinely performed by the cardiologist or echo technician to provide views of the heart.
High frequency sound, too high to hear, is beamed at the heart and the reflection is viewed as an image on a screen, rather like sonar in submarines.
As well as structural information about the heart, use of a technique called Doppler allows the speed and direction of blood in the heart to be ascertained, shown as a coloured image on the screen or as a waveform.
Useful website
Congenital & Children’s Heart Centre – https://www.childrensheartcentre.com/commoninvestigations/echocardiography.html